When I was a kid, I had a spare tire around my waist. It wasn’t always there but the love handles sprouted, like dandelions in the spring, when I was about 8. Being a little heavier than other kids, I put the blame on my metabolism. I didn’t even know what the metabolism was, I thought it was an organ and that mine wasn’t as powerful as others.
Fast forward now about 20 years, I’ve come to know the what the metabolism is (hint: it’s not an organ). I’ve also learned how much blame I can put on a slower metabolic process my body may or may not have and how to take ownership for my eating habits.
In this article, I’ll share with you what the metabolism is, benefits of improving the metabolism as well as what helps (and what doesn’t help) increase metabolism.
What Is The Metabolism

The metabolism is a series of chemical reactions in the body that produce energy. It’s not an organ or a single tissue but is the mitochondria in cells taking energy mainly from glucose (carbs), breaking it apart and capturing the energy that explodes out from each separation. That captured energy is stored in what’s called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Then the ATP molecules are used up in most reactions throughout the body.
The metabolism, and what helps boost metabolism, is linked to multiple factors including mitochondrial diversity, mitochondrial amount, genetics, enzymes, co-enzymes, micronutrients, ATP output potential and much more.
To summarize, the metabolism takes the food you eat, breaks it down and captures the energy within it to use. The metabolism is like a power plant because it takes raw material, breaks it down and then sends out the energy (electricity) to different parts of the body.
What Helps Increase Metabolism

Now that we’ve gone over the metabolic process, let’s jump into what helps increase metabolism.
Muscle
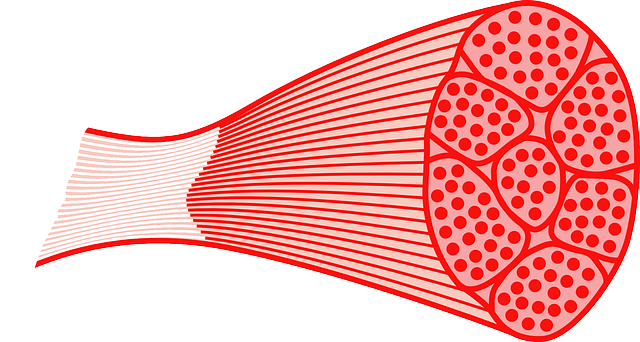
Skeletal muscle is one of the biggest metabolically demanding tissues and structures in the body. It helps increase resting metabolic rate and is a determinate for weight gain or obesity because of the amount relative to each individual.
You can’t grow more muscle fibers, those are locked in for the most part, but you can grow the muscle fibers bigger. As the muscle fibers grow bigger they will be demanding and burning more energy.
Keep in mind, you don’t have to be Arnold Schwarzenegger size to get the beneficial burning effects of larger muscles. Just a little more muscle will increase metabolism. And for you ladies out there, your gut reaction may be against putting on muscle but you can put on some muscle and not be “bulky” looking.
If you already have some extra fat on you then your instinct may be against putting on muscle but that’s counter productive. You WANT to put on muscle especially if you’re a little overweight because that added muscle will help you burn more calories.
Advice For Putting On Muscle
There’s a lot out there about having to eat a preposterous amount when putting on muscle. In my experience, that just leads to way more fat gain than any extra muscle being worth it. My fitness goals are above anything to look lean and feel vibrant, I don’t feel that way when I start putting on fat.
Instead of eating a ton of food, the focus should be on the workouts and quality protein. You can eat all the food you want but if you don’t stress and exercise your muscles in the right way it’ll never stimulate them enough to build up. Then that’s where quality protein comes into play, to help rebuild the muscle after it’s been broken down. Don’t get me wrong, you still need to find a good balance of carbs and fats but where most people go wrong is they don’t even get in the proper workout or have protein to recover from it.
Working Out: Be sure to hit the muscle groups you want to grow most 2x a week. An example of a muscle growing workout split is below, it doesn’t have to be exactly this because you can adjust it to your medium of exercise just be sure to have enough resistance twice a week.
- Day 1: Chest and Shoulders
- Day 2: Back and Biceps
- Day 3: Legs
- Day 4: Chest and Shoulders
- Day 5: Back and Biceps
High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)

HIIT is a fantastic way to increase the metabolism and burning effect. HIIT is basically short bursts of intense exercise with small rests in between. Example would be doing 6 explosive pushups, resting 20 seconds, then doing 2 more, resting 20 seconds then doing 2 more. Rest 30 seconds then do it again…etc.
Burn More During Workouts: When doing HIIT, the body is mostly using anaerobic (no oxygen) pathways to generate energy in the muscles. This uses significantly more glucose than aerobic (with oxygen) exercising such as cycling. Remember back to the beginning of this article when I explained what ATP is, it’s the energy molecules responsible for powering the body. Each one of these molecules gets produced by the metabolic process, in the anaerobic process only 2 ATP are generated from each glucose compared to about 36 ATP generated from the aerobic pathway. Basically, you’ll be using a lot more glucose during those short intense bursts than 30 minutes on the elliptical machine.
Increased Metabolism After: Not only are you burning more energy during HIIT workouts than others but there are studies showing HIIT keeps the resting metabolic rate higher after exercise as well.
There is a study that compared male students doing 2 minute sprints 3 times a week versus 30 minutes of traditional cardio 3 times a week. They found doing the sprints kept the metabolism increased post-exercise more than the traditional 30 minutes of cardio.
There’s another study that took 17 males and had them do either traditional resistance training or HIIT. They found that after 22 hours the HIIT group had more of an improve resting metabolic rate than the traditional resistance training group.
Sleep
Getting the right amount of sleep can enhance your metabolism but sleeping less than 6 hours or more than 10 hours has been shown to throw it off.
There was also a study that looked at sleep restricted people and examined the way their body utilizes fat after a fat-heavy meal. They found that sleep restricted people’s metabolism stored fat easier after a meal.
Lack of sleep also affects:
- Hunger Hormones: leptin (satiety hormone) gets down-regulated and ghrelin (appetite stimulating hormone) increases; you get hungrier and are less full with every meal.
- Cortisol levels: which can reduce the body’s ability to handle stress and therefore put on fat easier.
For those who don’t get the right amount of sleep, seeing research on how they should be getting more may not do much to help. So, instead of just putting the research out there I also want to share some tips on getting better sleep.
Tips For Better Sleep:
- Find the right temperature, colder temperatures may be better for sleep
- Take a hot shower/bath before bed to relax your body and muscles
- Listen to a guided meditation while sitting in bed
- Use Muse or other meditation tech/apps to help you meditation for 10 minutes before bed to reduce stress and put you in a calm state of mind
- Listen (audio only, Spotify for example, don’t watch shows or TV due to blue light exposure) to a few stand up comedy skits for 10 minutes to lighten your mood before bed
Metabolism Questions Answered

I’ll go through some common questions about metabolism for substances that either may, or may not, work but didn’t make the list for what helps boost metabolism for various reasons.
How Often Should I Eat To Increase Metabolism?
There are resources that say to eat smaller meals more frequently to increase the metabolism. While that may be true, the boost to metabolism is insignificant compared to the amount of extra calories potentially consumed throughout the day by implementing this strategy. Ergo, it’s not worth eating several small meals in the day, unless you’re measuring out each one and deliberately eating those small meals without consuming anything extra.
Eating 3 meals a day with 1 snack is fine.
Does Water Speed Up Metabolism?
Yes, there have been studies that show water can speed up metabolism. Water can raise the metabolic effect and burn around 23 to 100 extra calories a day. However, I’m not including it on the list of what helps increase metabolism because in those studies, the amount of water people drink is basically the recommended amount of water humans should be drinking daily anyways. It’s not a big enough strategy to use to boost metabolism that’s out of the norm.
Does Green Tea Speed Metabolism?
Maybe, but the effects won’t be significant. There’s been different studies and reviews on how much green tea can increase metabolism. Some show it may have a small increase in metabolism, while others don’t cite any boost and most say it’s not significant enough even if it does. For that reason, ‘does green tea speed metabolism’ didn’t make the list of what helps increase metabolism.
Does Spicy Food Speed Up Metabolism?
Maybe by a tiny amount. There’s been many studies on it, one review in particular examined multiple reviews and studies to show that having spicy food can help but only about 10 extra calories per meal. Over about 6 years that’s only 1 pound lost; you could easily lose 1 pound in 1 month with HIIT. I personally don’t think that’s significant enough to put down because that would mean at EVERY meal for 6 years you’d have to have something spicy to lose just 1 pound…
Summary
The metabolism is a series of chemical reactions in the body that utilize resources for energy in the form of ATP molecules.
What Helps Increase Metabolism:
- Muscle
- HIIT Workouts
- Sleep
Others that can help increase metabolism but either have too much conflicting research or won’t be significant enough to create a strategy around or worth implementing on a long-term basis.
- Water
- Green Tea
- Spicy Foods
Disclaimers
I am not a doctor and do not recommend anything on this site, or blog post, for anyone without consulting with their doctor first. Please read the privacy policy for more information.
The information in this article is for educational and entertainment reasons, it should not be interpreted as medical advice or as a recommendation for a specific treatment. Always talk to your doctor and in the event of a medical emergency one should seek the help of a qualified and licensed health care provider.
You should understand that when participating in any exercise or exercise program, there is the possibility of physical injury. If you engage in this exercise or exercise program, you agree that you do so at your own risk, are voluntarily participating in these activities, assume all risk of injury to yourself, and agree to release and discharge Thefitnesswrangler.com from any and all claims or causes of action, known or unknown, arising out of Thefitnesswrangler.com
There are affiliate links in this post where we’ll get a paid fee if you purchase something from that link – it won’t cost any more to you and in some cases may even save you money.











Leave A Comment